An Absolutely Superb Esoteric Antique Witchcraft Fetish Statue. An African Kongo Witch Doctor's Nail-Fetish Figure, A Voduo {Voodoo} Nkondo Nkisi. Historically Much Feared by Victorian Missionaries as Instruments of Sorcery. Made by The Tribal Nganga
In the world of art collecting, original rare African tribal carvings of Mangaaka Power figures such as this,are about as desirable one can get.
Some of the most valuable collections of such Mangaaka Power figures etc. {from the 1880's to 1900's} in the world, are now in the Met or Smithsonian in America, donated by such as the Michael C. Rockefeller wing collection by Nelson Rockefeller.
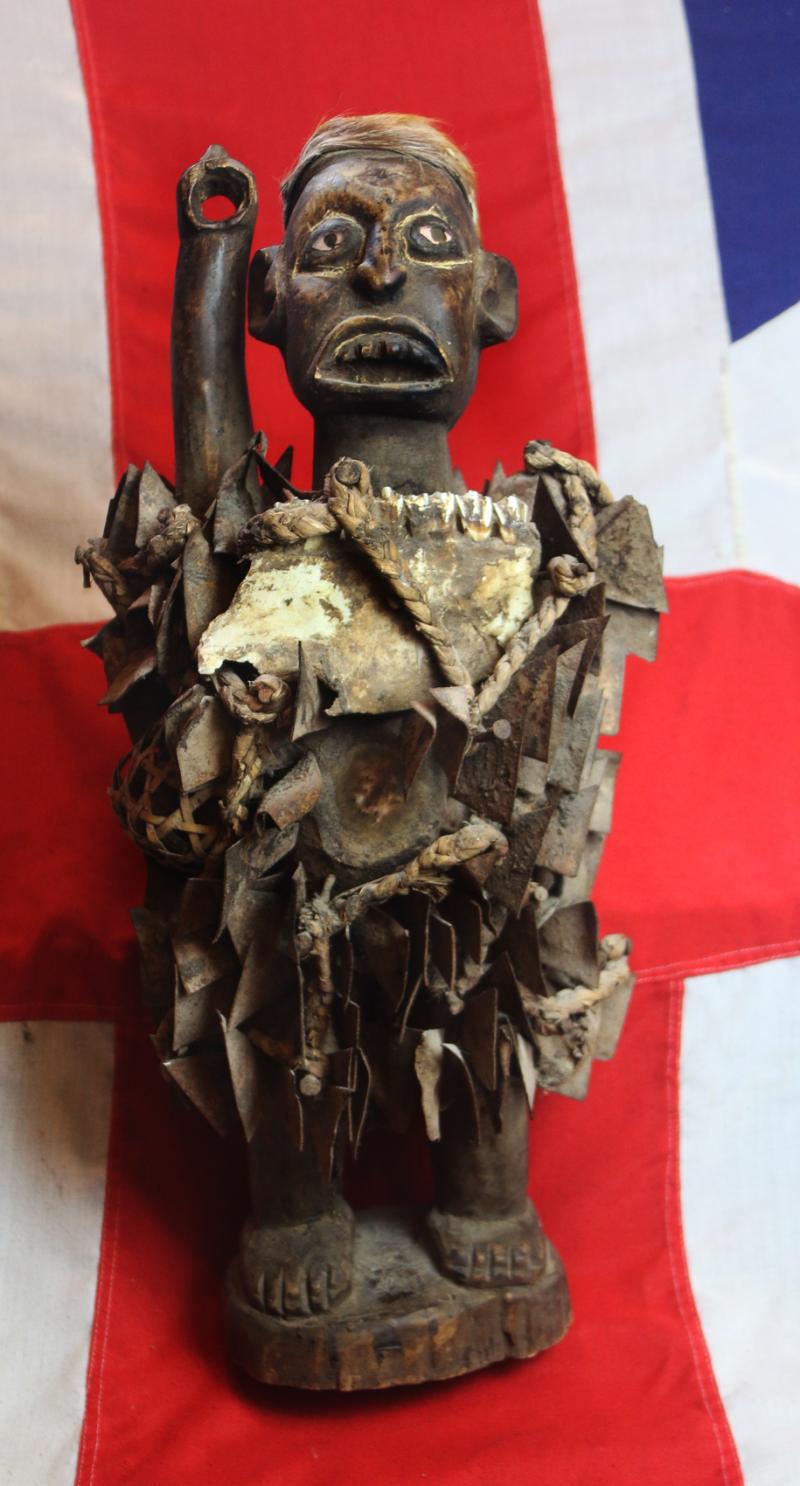
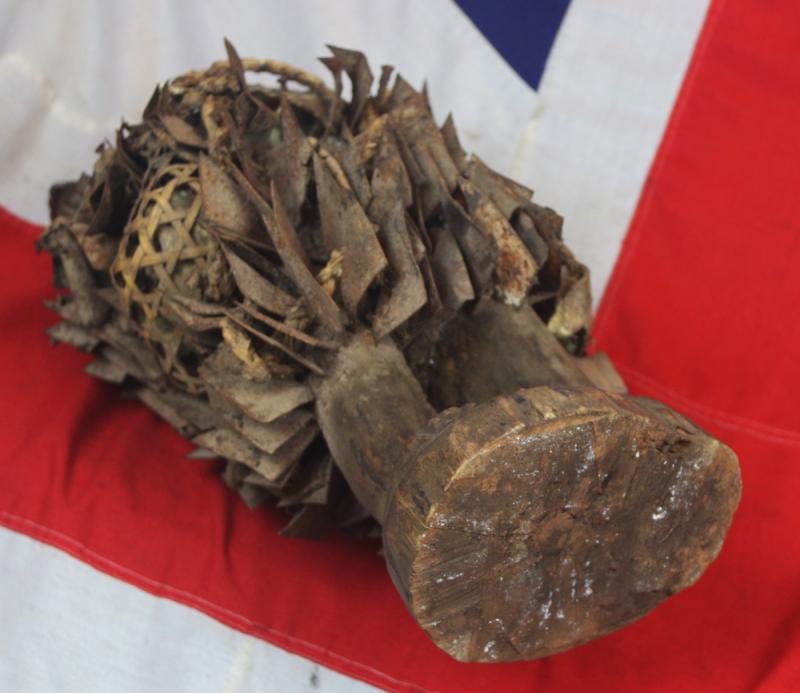
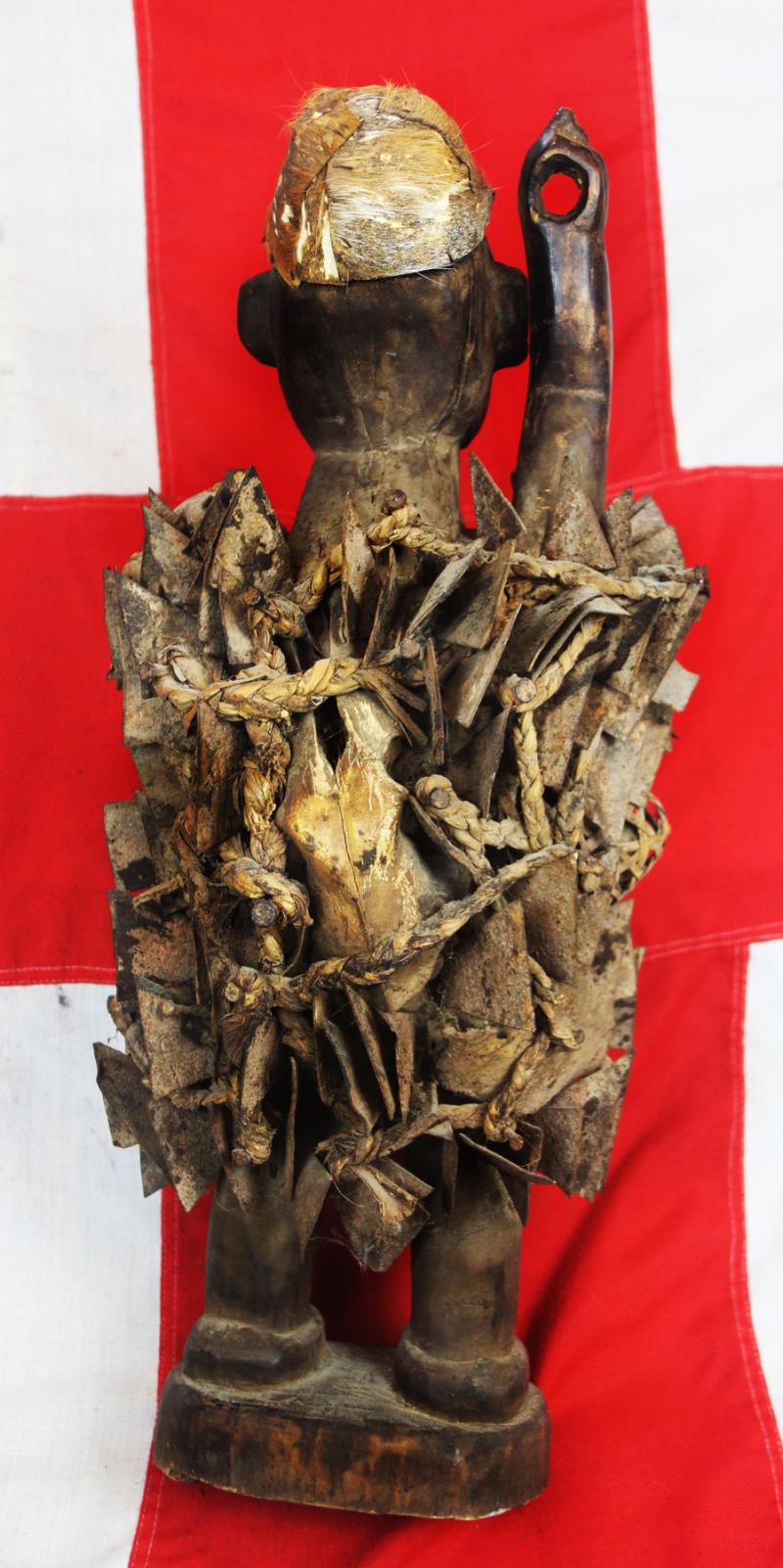
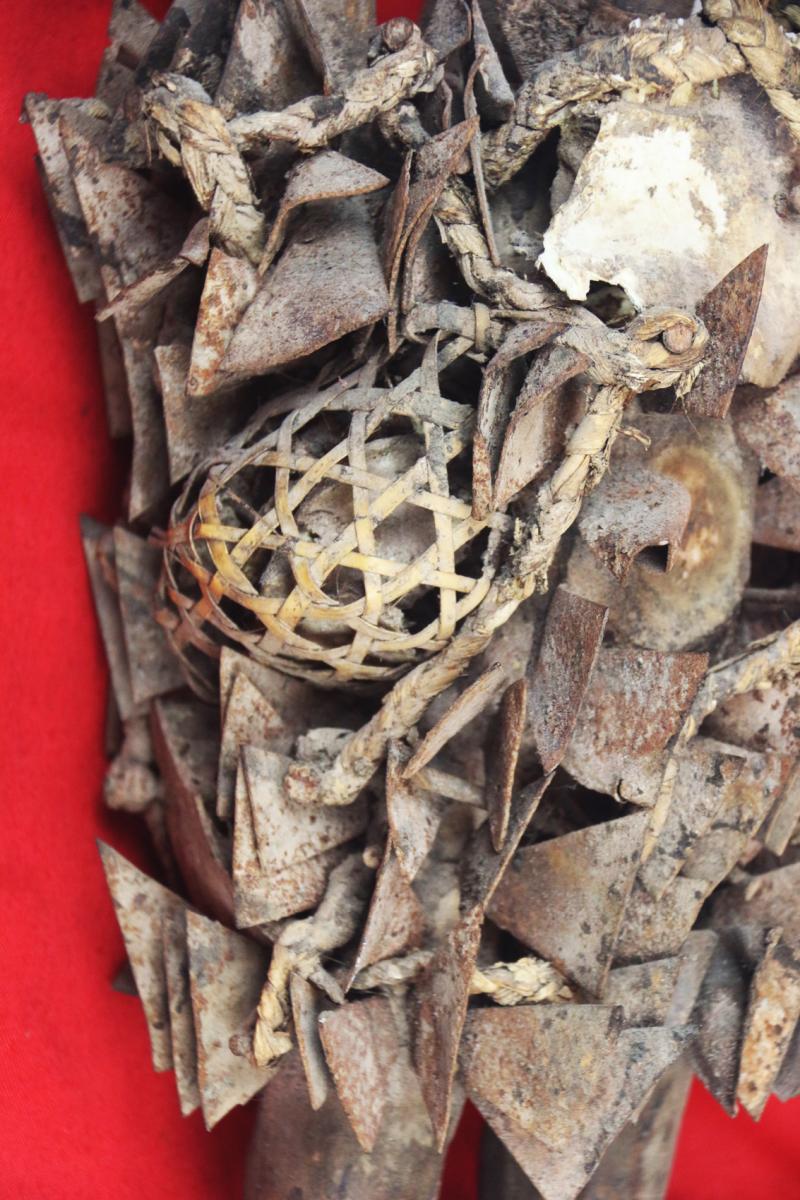
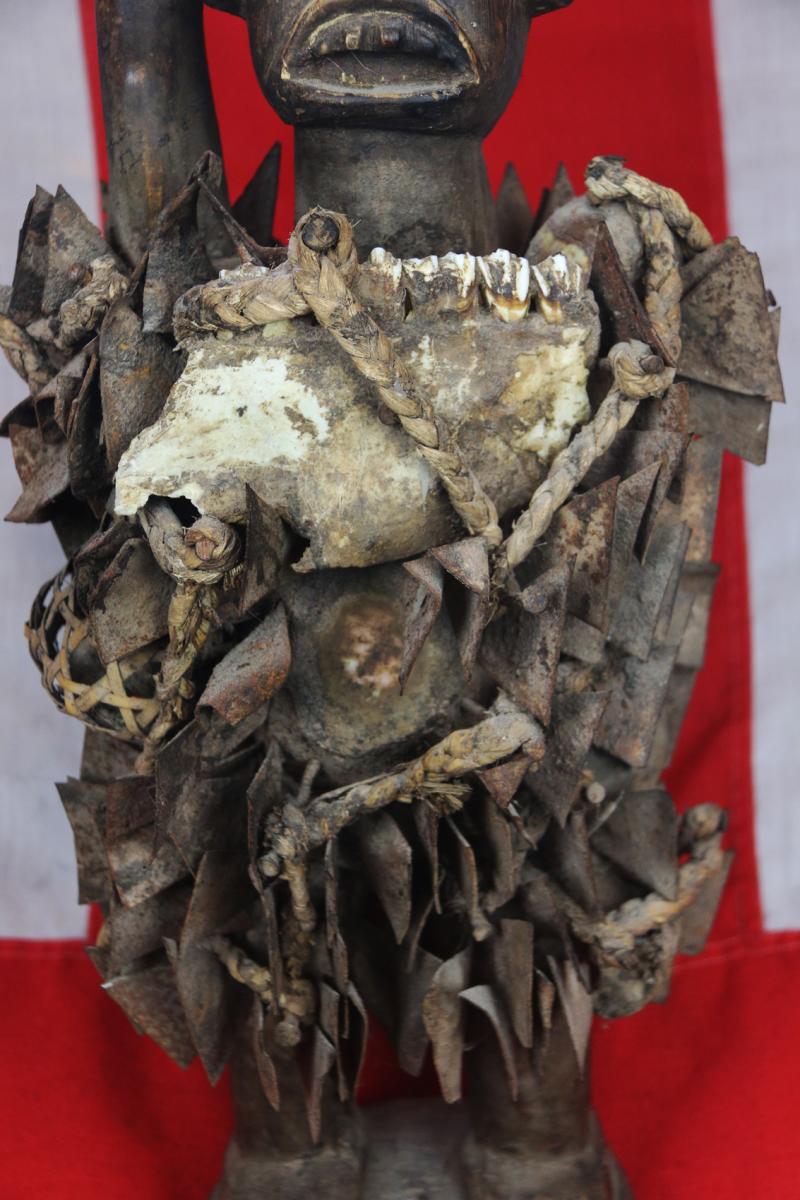
The African Kongo Witch Doctor's power figures minkisi {plural of nkisi} that stand prominent among all minkisi is called nkisi {sacred medicine} nkondi {hunter} likely from the Bakongo people. This type of figure is commonly called a nail fetish and is one of the most recognisable and collectible figures in all of African art. These life-like figures are instantly identified by the many nails, pegs, blades, and shards that are hammered into them and made by the tribal Nganga { Witch Doctor } .
Each individual insertion represents one of three things: an oath or agreement between two parties, a pledge to provide protection against enemies and witchcraft, or a vow of vengeance. 'Nkondi' literally means 'hunter;' and it is generally considered an aggressive entity.
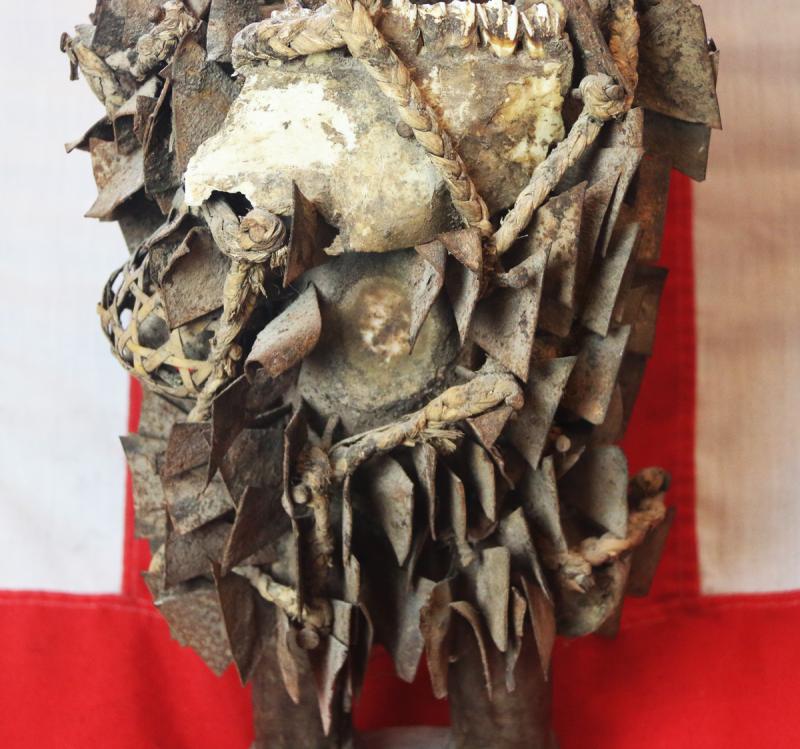
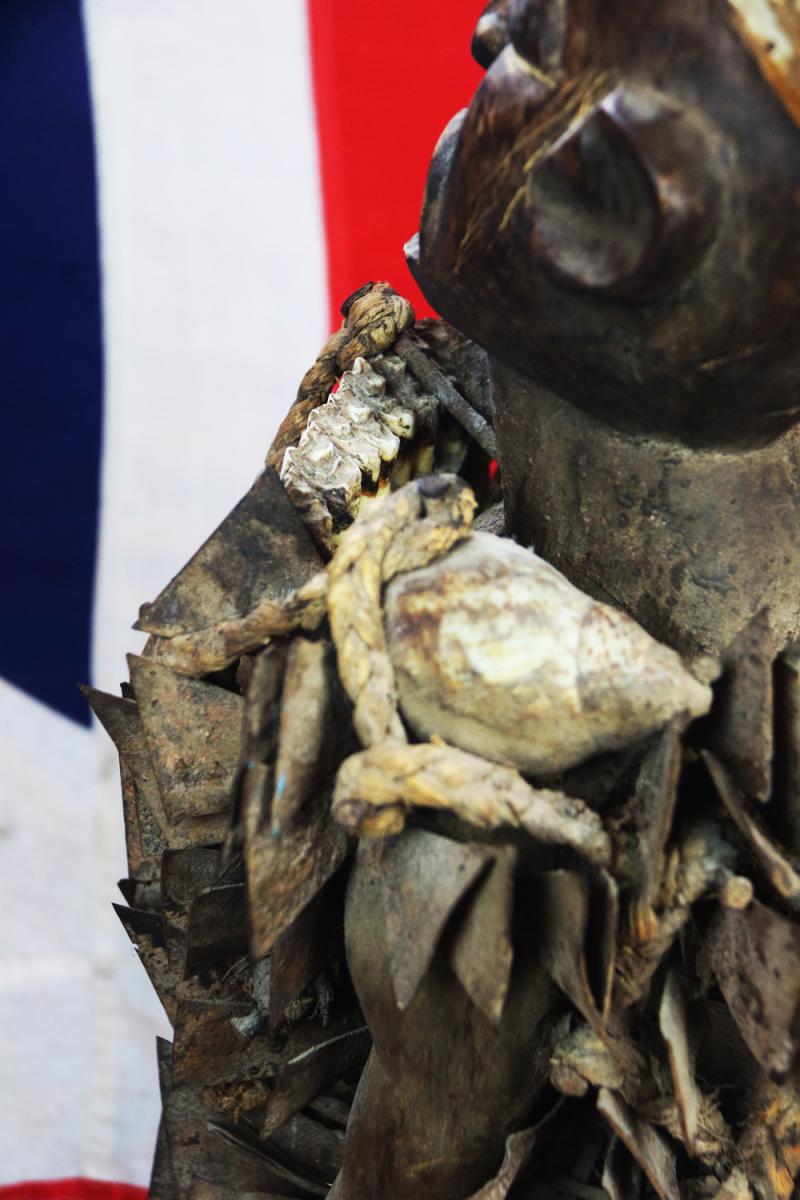
The insertions are driven into the figure by the nganga and represent the mambu and the type or degree of severity of an issue can be suggested through the material itself. A peg may refer to a matter being ‘settled’ whereas a nail, or metal shard, deeply inserted, may represent a more serious offense such as murder. Prior to insertion, opposing parties or clients often lick the blades or nails, to seal the function or purpose of the nkisi through their saliva. If an oath is broken by one of the parties or evil befalls one of them, the nkisi nkondi will become activated to carry out its mission of destruction or divine protection
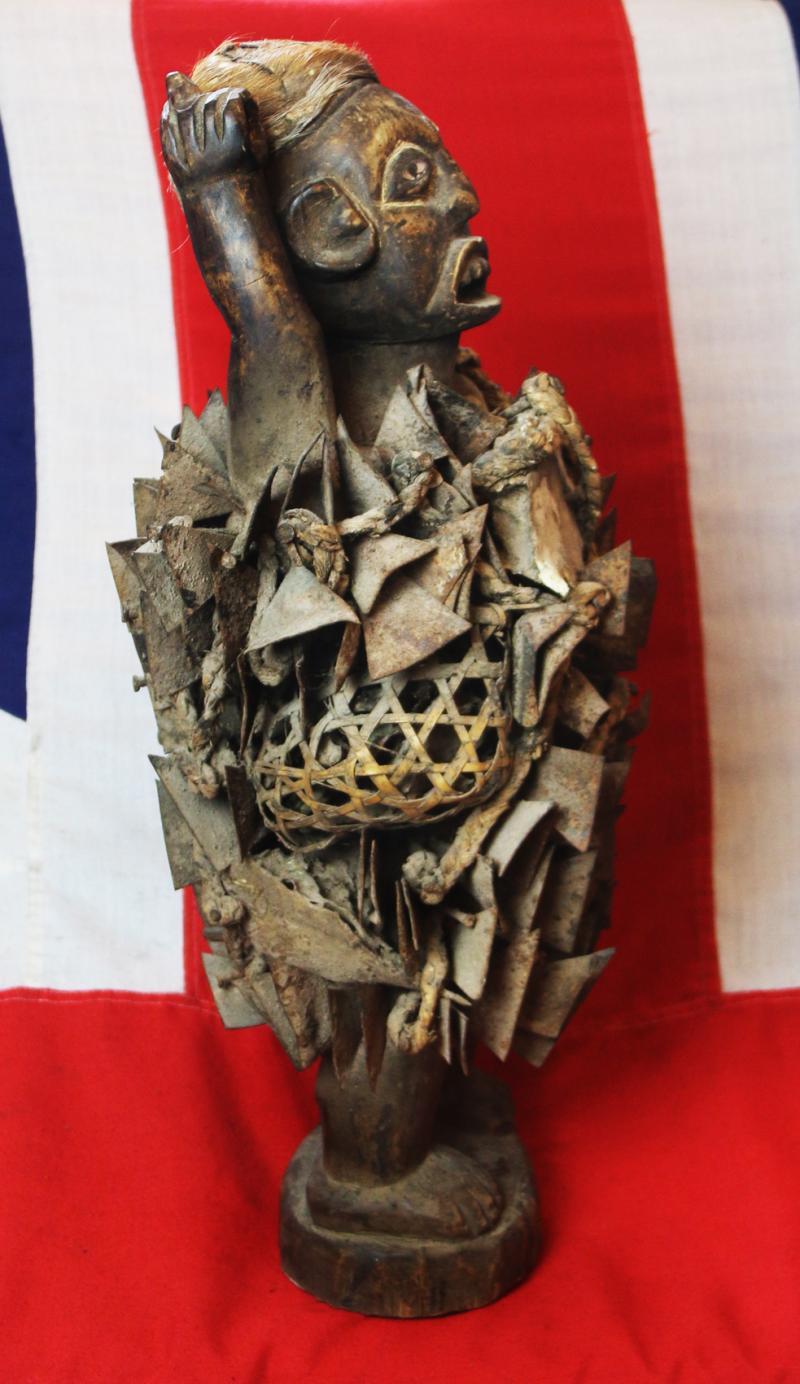
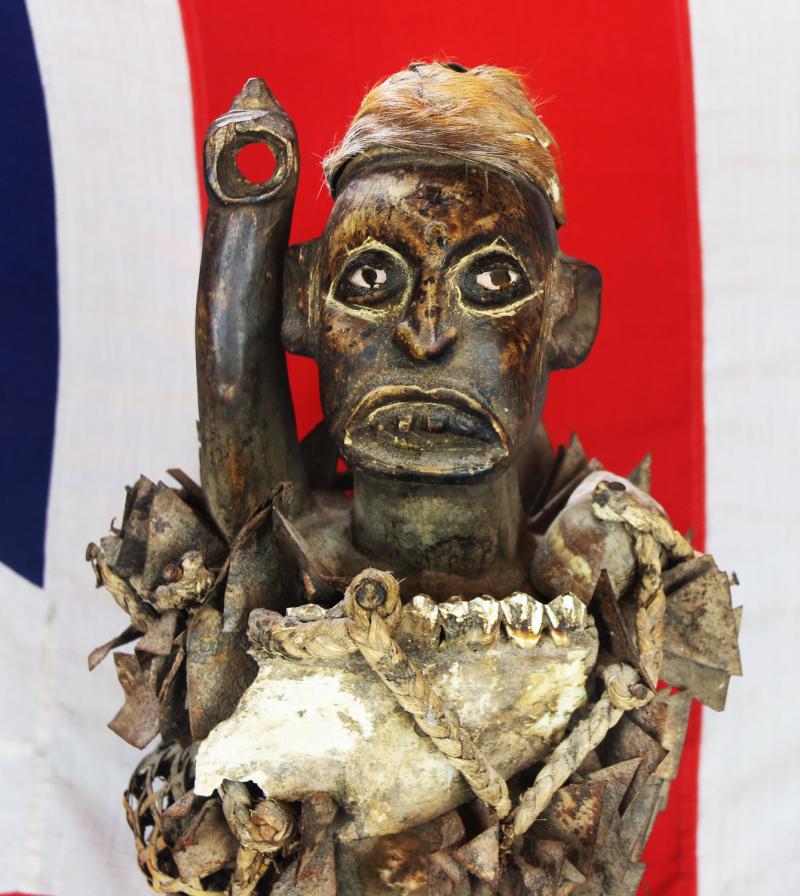
The imposing presence and implied power of nkisi nkondi is certainly enough to keep anyone committed to a promise or agreement. Like other minkisi, powerful medicine is usually stored inside the belly, which can then covered by a piece of glass or mirror. The reflective surface represents the world of the dead and the vision of the spirits. One is a traditional naked fetish witchcraft figure, standing upright, deeply carved staring eyes a the body studded overall with hundreds of sharp shards of iron driven into the body, a traditional oath taking figure, with its right arm outstretched, upwards that may, some believe, have once held a spear.
A nkisi has many interrelated functions. African doctors use it to effect healing. They use the nkisi to search for the spiritual and physical source of a malady and then chase it away from the body. As a preventive measure, spiritual leaders also use it to protect the human soul, guarding it against disease and illness. In addition, they may use it to bind its owner to a friend or to attract lovers. It is also used to serve as a charm to repel enemies, arrest them in their tracks, or inflict an illness on them. Alternatively, a nkisi can be used to embody and direct a spirit; similarly, it can be used as a hiding place for a troubled soul, keeping order.
Nkisi, in west-central African lore, any object or material substance invested with sacred energy and made available for spiritual protection. One tradition of the Kongo people of west-central Africa holds that the god Funza gave the world the first nkisi. Africans uprooted during the Atlantic slave-trade era carried with them some knowledge of nkisi making. In places throughout the United States, particularly in the Deep South, African descendants still create minkisi. Nkisi making is also found throughout the Caribbean and South America, in places such as Cuba, Haiti, and Brazil.
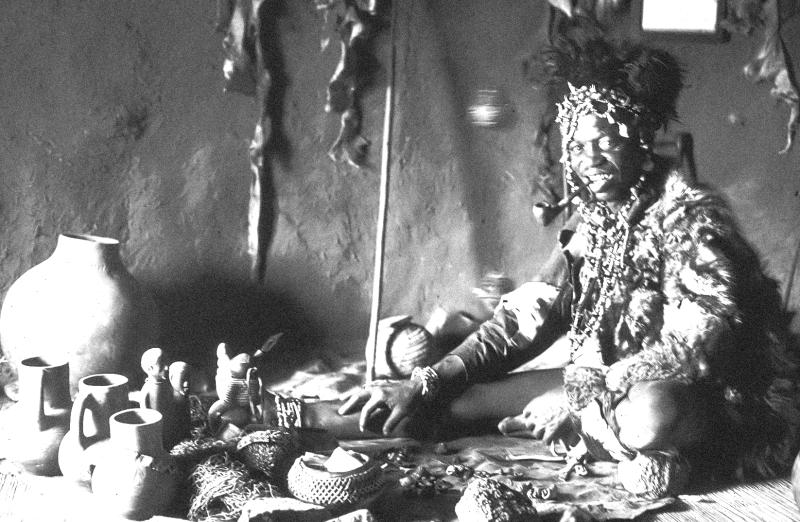
This wild appearance of the Nganga was intended to create a frightening effect, or kimbulua in the Kongo language. The nganga's costume was often modeled on his nkisi. The act of putting on the costume was itself part of the performance; all participants were marked with red and white stripes, called makila, for protection.
The "circles of white around the eyes" refer to mamoni lines (from the verb mona, to see). These lines purport to indicate the ability to see hidden sources of illness and evil.
Yombe nganga often wore white masks, whose color represented the spirit of a deceased person. White was also associated with justice, order, truth, invulnerability, and insight: all virtues associated with the nganga.
The nganga is instructed in the composition of the nkondi, perhaps in a dream, by a particular spirit. In one description of the banganga's process, the nganga then cuts down a tree for the wood that s/he will use to construct the nkondi. He then kills a chicken, which causes the death of a hunter who has been successful in killing game and whose captive soul subsequently animates the nkondi figure. Based on this process, *Gell writes that the nkondi is a figure an index of cumulative agency, a "visible knot tying together an invisible skein of spatio-temporal relations" of which participants in the ritual are aware
After a tribal carver artist completed carving the artifact, the "nganga" transformed it into an object capable of healing illness, settling disputes, safeguarding the peace, and punishing wrongdoers. Each work of this kind or "nkisi" is associated with a spirit, that is subjected to a degree of human control.
Europeans may have encountered these objects during expeditions to the Congo as early as the 15th century. However, several of these fetish objects, as they were often termed, were confiscated by missionaries in the late 19th century and were destroyed as evidence of sorcery or heathenism. Nevertheless, several were collected as objects of fascination and even as an object of study of Kongo culture. Kongo traditions such as those of the nkisi nkondi have survived over the centuries and migrated to the Americas and the Caribbean via Afro-Atlantic religious practices such as vodun, Palo Monte, and macumba. In Hollywood these figures have morphed into objects of superstition such as New Orleans voodoo dolls covered with stick pins. Nonetheless, minkisi have left an indelible imprint as visually provocative figures of spiritual importance and protection.
Often such figures were placed outside, or within, the hut of a certain form of tribal elder, what we would refer to as, the tribal witch-doctor, called a Nganga as a symbol of his position within the local village, and his ability to cause magical curses and unpleasantness for villagers who had fallen out with others of the village or region, who then sought out the services of the so called 'witch-doctor' to resolve the problem, with, such as, a curse.
Vintage Hand Carved African Medicine Man Nkisi figures. Esoteric collector's pieces, connected to the so-called western term of Voodoo {vodou} magic, part of the pantheon of the occult, magic & witchcraft of Africa.
Among the various Kongo peoples, nkisi means a sacred medicine. This word has been extended to include objects containing that medicine as well. The carved wooden statues referred to in the 19th century as nail fetishes and more recently as power figures containing medicine that imbues them with divine power, are therefore nkisi as well. Due to the medicine they contain (which is administered by a witch doctor or nganga), they act as agents of divine power, granting requests. healing or attesting to agreements. Each decision or resolution is literally nailed down in the figure.
A certain class of nkisi, called nkondi, are able to enforce the solutions they provide actively and to seek vengeance against those who heed them not. These figures either menace the viewer with spears and fierce facial expressions, or strike intimidating, belligerent poses.
Nkisi nkondi specialize in different areas of life. The most important nkisi nkondi carries out mangaaka, or preeminent justice.
Surveillance or watchfulness assist the effective enforcement of the power figure’s decisions. This is registered in the size of the eyes or, in some cases, by multiple sets of eyes. The rope wrapped around some figures represents a snake, a watchful predator who lends its powers of observation to the figure. Double-headed figures have double the visual powers and can see into the city of the dead and the realm of the living at the same time.
Each power figure has a distinct personality, ranging from contemplative to angry to soulful to reserved to compassionate. The ability to suggest those qualities visually with such immediacy and precision is one of the most impressive aspect of the surviving figures.
Kongo religion Kikongo: Bukongo. Bakongo religion was translocated to the Americas along with its enslaved practitioners. Some surviving traditions include conjure, dreaming, possession by the dead to learn wisdom from the ancestors, traditional healing and working with minkisi. The spiritual traditions and religions that have preserved Kongo traditions include Hoodoo, Palo Monte, Lumbalú, Kumina, Haitian Vodou, Candomblé Bantu, Kongo traditions such as those of the nkisi nkondi have survived over the centuries and migrated to the Americas and the Caribbean via Afro-Atlantic religious practices such as vodun, Palo Monte, and macumba.
Similar examples in the Smithsonian and Metropolitan in the USA. One very similar nkisi, from the late 19th to mid 20th century has been a highlight of the Rockefeller collection since its acquisition in 1952.
*Gell, A . The Art of Anthropologie. London: Humanities Press.
Code: 25498
2795.00 GBP