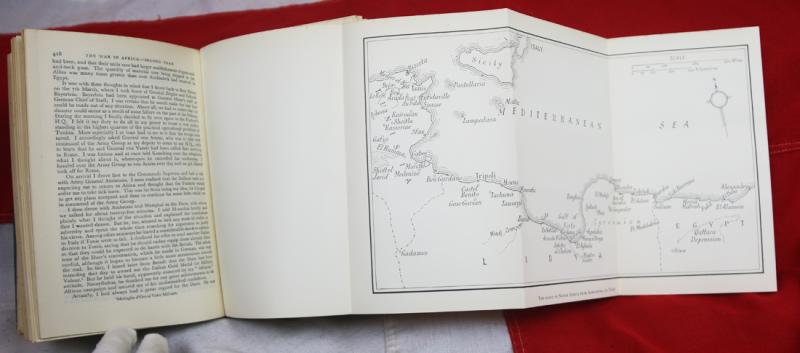
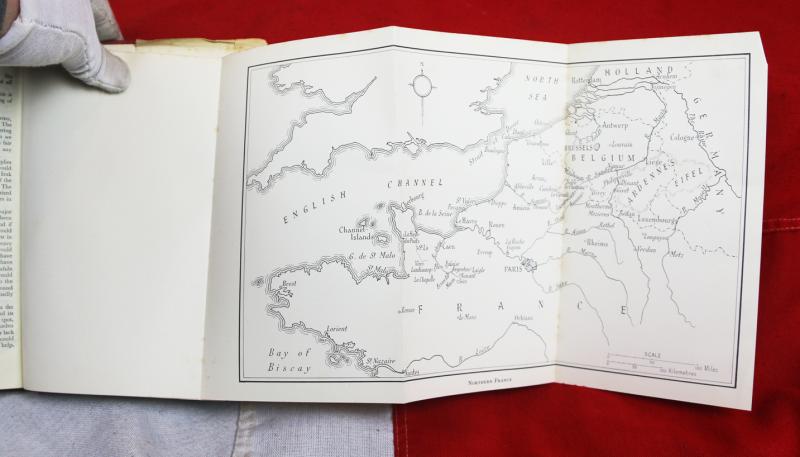
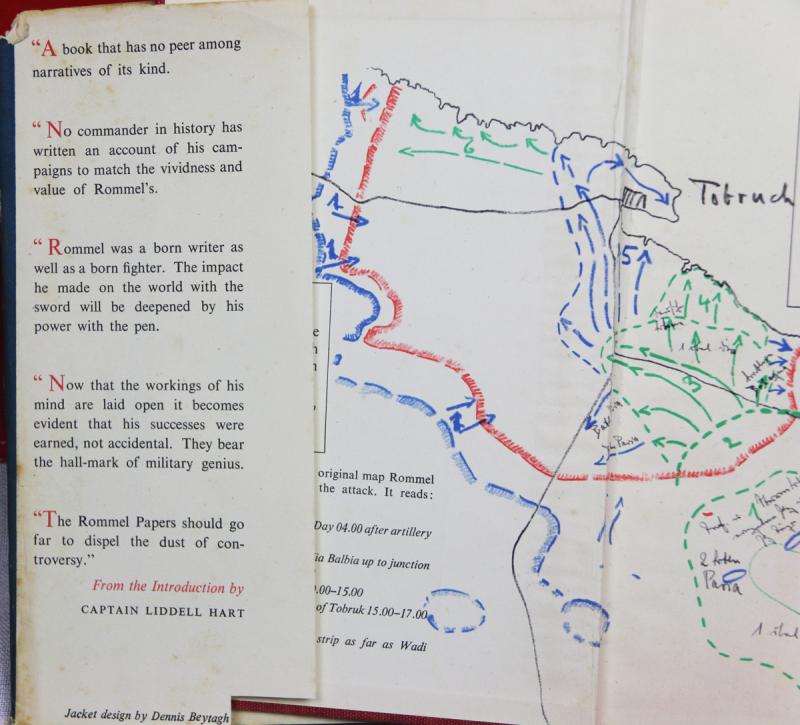
Ist Edition of 'The Rommel Papers' Printed by Collins in 1953
The Rommel Papers is the collected writings by the German World War II field marshal Erwin Rommel published in 1953.
A good volume example of the career and tactics of one of the greatest and revered generals of the war. In fact even Winston Churchill announced his demise in parliament, as the death of a noble leader of men that was not tainted, unlike many others in Germany, by the NAZI disease and corrupt influences of the Third Reich.
The book included Rommel's writings of the war, edited by the British journalist and historian B. H. Liddell Hart, the former Wehrmacht officer Fritz Bayerlein, who served on Rommel's staff in North Africa, and Rommel's widow and son. The volume contained an introduction and commentary by Liddell Hart.
Liddell Hart had a personal interest in the work: by having coaxed Rommel's widow to include material favourable to himself, he could present Rommel as his "pupil" when it came to mobile armoured warfare.
Thus, Liddell Hart's "theory of indirect approach" became a precursor to the German blitzkrieg ("lightning war"). The controversy was described by the political scientist John Mearsheimer in his work The Weight of History, who concluded that, by "putting words in the mouths of German Generals and manipulating history", Liddell Hart was in a position to show that he had been at the root of the dramatic German successes in 1940.
The historian Mark Connelly argues that The Rommel Papers was one of the two foundational works that lead to a "Rommel renaissance" and "Anglophone rehabilitation", the other being Desmond Young's biography, Rommel: The Desert Fox. The book contributed to the perception of Rommel as a brilliant commander; in an introduction, Liddell Hart drew comparisons between Rommel and Lawrence of Arabia, "two masters of desert warfare"
In World War II, he commanded the 7th Panzer Division during the 1940 invasion of France. His leadership of German and Italian forces in the North African campaign established his reputation as one of the ablest tank commanders of the war, and earned him the nickname der Wüstenfuchs, "the Desert Fox". Among his British adversaries he had a reputation for chivalry, and his phrase "war without hate" has been uncritically used to describe the North African campaign. A number of historians have since rejected the phrase as a myth and uncovered numerous examples of German war crimes and abuses towards enemy soldiers and native populations in Africa during the conflict. Other historians note that there is no clear evidence Rommel personally was involved or aware of any of these crimes, with some pointing out that the war in the desert, as fought by Rommel and his opponents, still came as close to a clean fight as there was in World War II. He later commanded the German forces opposing the Allied cross-channel invasion of Normandy in June 1944.
With the Nazis gaining power in Germany, Rommel gradually accepted the new regime. Historians have given different accounts of the specific period and his motivations. He was a supporter of Adolf Hitler, at least until near the end of the war, if not necessarily sympathetic to the party and the paramilitary forces associated with it. In 1944, Rommel was implicated in the 20 July plot to assassinate Hitler. Because of Rommel's status as a national hero, Hitler wanted to eliminate him quietly instead of having him immediately executed, as many other plotters were. Rommel was given a choice between suicide, in return for assurances that his reputation would remain intact and that his family would not be persecuted following his death, or facing a trial that would result in his disgrace and execution; he chose the former and took a cyanide pill. Rommel was given a state funeral, and it was announced that he had succumbed to his injuries from the strafing of his staff car in Normandy.
Rommel became a larger-than-life figure in both Allied and Nazi propaganda, and in postwar popular culture. Numerous authors portray him as an apolitical, brilliant commander and a victim of Nazi Germany, although this assessment is contested by other authors as the Rommel myth. Rommel's reputation for conducting a clean war was used in the interest of the West German rearmament and reconciliation between the former enemies – the United Kingdom and the United States on one side and the new Federal Republic of Germany on the other. Several of Rommel's former subordinates, notably his chief of staff Hans Speidel, played key roles in German rearmament and integration into NATO in the postwar era. The German Army's largest military base, the Field Marshal Rommel Barracks, Augustdorf, and a third ship of Lütjens-class destroyer of the German Navy are both named in his honour. His son Manfred Rommel was the longtime mayor of Stuttgart, Germany and namesake of Stuttgart Airport.
Code: 25106