Most Rare, Original Pair of Napoleonic War Period Issued Medals, The Prussian & Bavarian Battle of Waterloo & Battle of Leipzig, One Made From Captured Cannon, Just as The British Victoria Cross Was Made From Captured Russian Cannon.
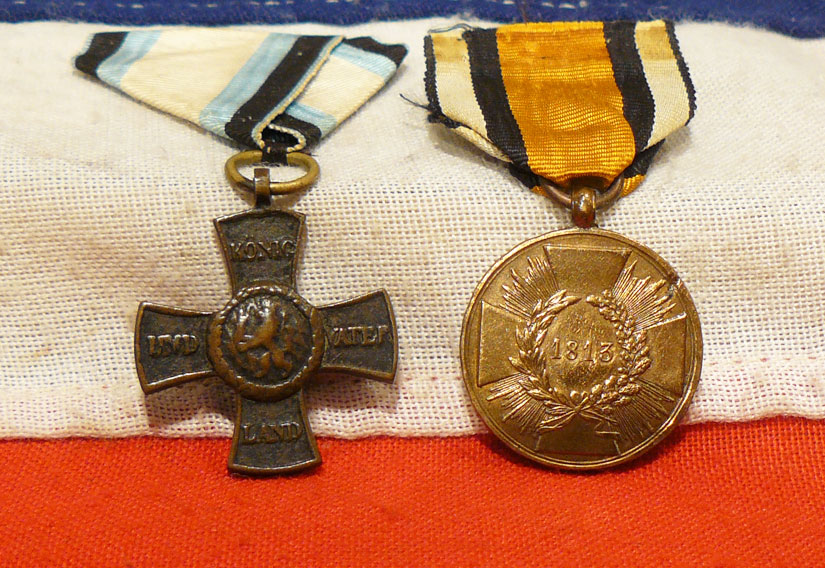
Really rare to find, but exceptionally good value when one considers the British equivalent for two original medals for the Napoleonic campaigns would be between five and ten times this price. The Prussian Campaign Medal for 1813, a cross within a circle, made from captured cannon, and the Bavarian Military Campaign Medal for the Napoleonic Wars in 1813, 1814, 1815, for Officers and Other Ranks, awarded in 1817-1818.
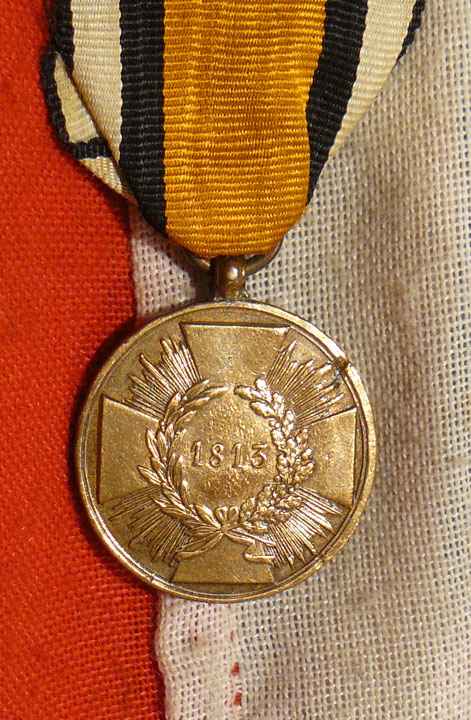
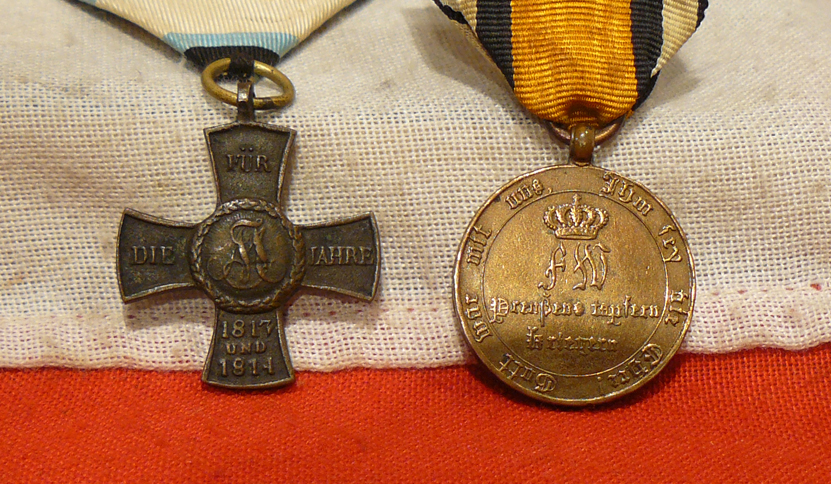
Prussian Medal; Circular bronze medal with loop for ribbon suspension; the face with a cross pattee with rays between the arms, the date 1813 centrally within a laurel wreath; the reverse with the crowned cypher of Friedrich Wilhelm III above the inscription Preusens tapfern kriegern (Prussia's brave warriors) circumscribed Gott war mit uns, Ihn sey die Ehre (God was with us To Him the Glory); the edge inscribed AUS EROBERTEM GESCHUTZ (from captured cannon); some surface wear; on an old correct ribbon. The medal was instituted by King Friedrich Wilhelm III at Frankfurt-am-Main on 24 December 1813 and amended on 3 October 1815 to be awarded to all warriors who without exception, whether in the field or before a fortress, truly fought and uncompromisingly did their duty throughout this current conflict? (jeden Krieger ohne Ausnahme, der im Felde oder vor einer Festung wirklich mitgefochten und der wehrend der Dauer des jetzigen Krieges seinen Pflichten treugeblieben ist). The medal exists with the dates 1813, 1814, 1813/1814 and 1815 and with square and rounded ends to the cross. Prussia was a key member of the coalition that fought Napoleonic France and its allies, culminating with victory at Waterloo on 18 June 1815. Bavarian medal; Bronze cross pattee alise with loop for ribbon suspension; the face with a circular central medallion bearing the cipher of King Maximilian I Joseph within an oak leaf border, the upper, left, right and lower arms inscribed FUR DIE JAHRE 1813 / UND / 1814 respectively; the reverse with a circular central medallion bearing the Bavarian lion on a lozenge ground within an oak leaf border, the upper, left, right and lower arms inscribed KONIG UND VATERLAND (King and Fatherland) respectively; on replaced correct ribbon. The Medal was instituted on 4 December 1814 and confirmed in statutes on 25 May 1817 to be awarded to Bavarian military who fought in the Napoleonic Wars. 16 June 1815
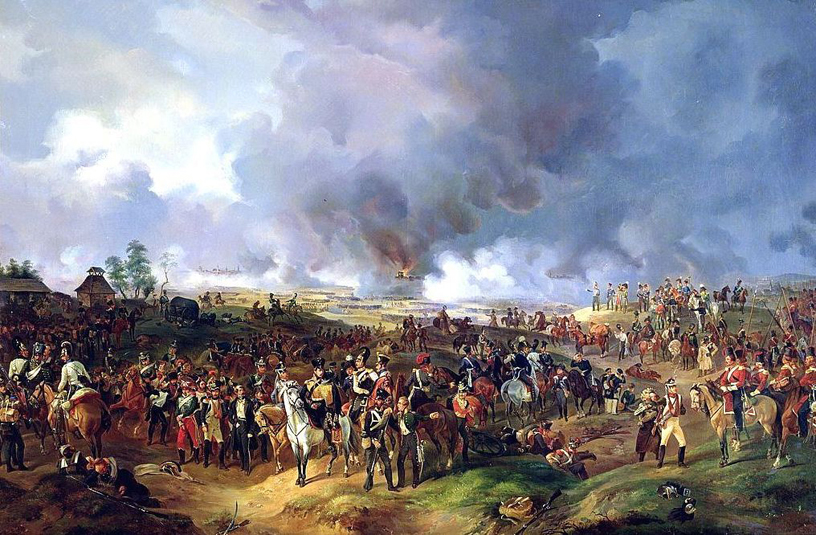
Wellington and Blucher meet at the windmill of Bussy at 1 pm, where they agree that Napoleon seems to be about to attack Ligny, not Quatre-bras. The Prussians take responsibility for this battle, but the 4th corps, headed by General von Bulow, doesn't arrive in time, and the 80,000-strong Prussian army loses the Battle of Ligny against Napoleon. Blucher is injured in the attack when his horse is shot from underneath him.
Later that same afternoon, the French Marshal Ney leads an attack at Quatre-Bras against the British, but the latter's superior numbers and French indecision allow them to avoid defeat.
17 - 18 June 1815
Though badly mauled on 16 June, Blucher retreats not east towards Prussia but re-establishes his position around Wavre (north and east from Ligny), thereby staying in contact with the allied force which had retreated from Quatre-Bras to Waterloo.
One of Wellington's ADCs reaches Blucher at 11 pm on 17 June, informing the Prussian general that the British general would fight a defensive battle at Waterloo. Blucher, after consultation with Gneisenau, resolves to send Bulow's 4th corps to attack the enemy's right flank. This would be followed by the 2nd corps, with the 1st and 3rd held in reserve. The 4th, 2nd and 1st corps march in two columns from Wavre towards the battlefield at Waterloo. Whilst Blucher was to hold the French off at Wavre, Bulow and Pirch II were to lead the left column (that which would finally take Plancenoit, to the rear of Napoleon's right) and Zieten on the right column would finally emerge onto the battlefield alongside Wellington's left round about 7 pm.
Though the battle at Plancenoit was to be hard fought, the Prussians eventually overrun the French right, causing the French army to turn and flee. Blucher was famously to meet Wellington on the battlefield between 9 and 10 pm, close to the Belle-Alliance farm, where the Prussian general used the only French he knew: 'Quelle affaire !' are the words that history has recorded.
Given the battering the Allied army had received throughout the day, the relatively fresh Prussian troops were to take the lead in pursuing the fleeing French troops. The Prussians had nevertheless lost 7,000 men. Napoleon's carriage was to be seized by Prussian cavalry at Gemappes, and the routed French were to be given no quarter by the furious Prussian pursuit. Blucher's advance guard was finally to reach the outskirts of Paris on 29 June. With Napoleon's abdication on 22 June, the war would officially end upon the signature of the Convention of St-Cloud on 3 July 1815. The Bavarian story from 1813 up to 15. King Maximillan I Josef turned with a heavy heart away from the French and changed to the Allied camp shortly before the Battle of Leipzig. The attempt by Wrede to stop the victory of the Grande Armee in 1813 at the Battle of Hanau ended in a narrow defeat for his Austro-Bavarian corps. The campaign of 1814 began badly for the Allies, but Wrede made up for his earlier defeat with valuable victories over his former allies at the battles of Arcis-sur-Aube and Bar-sur-Aube.
In 1814, the Bavarian army consisted of a Grenadier Guard regiment, 16 regiments of Line Infantry, two battalions of Jager, seven regiments of light cavalry (of which one was territorial), one regiment of Uhlans, two Hussar regiments, one regiment of Garde du Corps (mounted royal bodyguard), two regiments of foot artillery and one of horse-artillery.
In 1815, the 7th (National) Light Cavalry regiment was formed into two Cuirassier regiments. A very early pair of Napoleonic Wars Germanic Kingdom medals from the Napoleonic Wars. By comparison these medals are extremely inexpensive for the equivalent, British Waterloo medal is now anything up 8,000 plus depending on regiment etc..
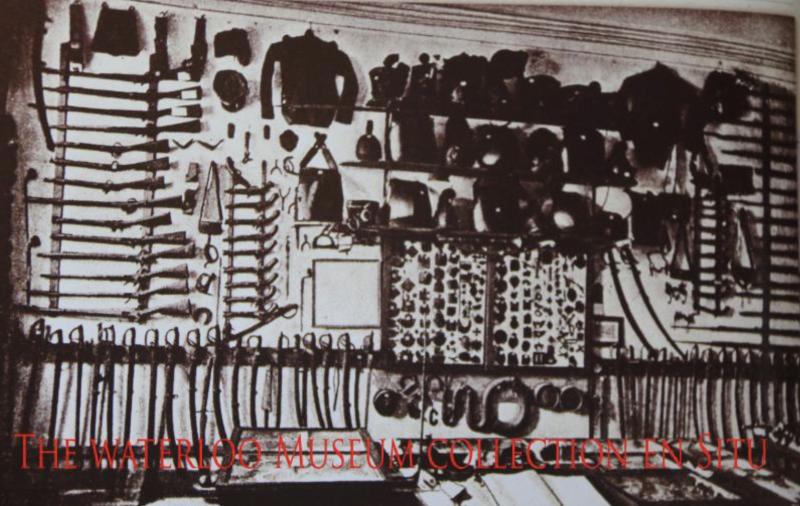
The last photo in the gallery shows a photograph of one section of the collection in the museum of Waterloo, taken in around 1900, showing all the weapons of Waterloo en situ, including all the protagonists {British, French, Prussian and Belgian muskets, swords, pistols, armour uniforms, etc}. The museum was founded and owned by a veteran of the 7th Hussars that fought at Waterloo
Code: 22369
1295.00 GBP